Downregulation of microRNA-34 induces cell proliferation and invasion of human mesothelial cells
$ 6.50 · 5 (382) · In stock
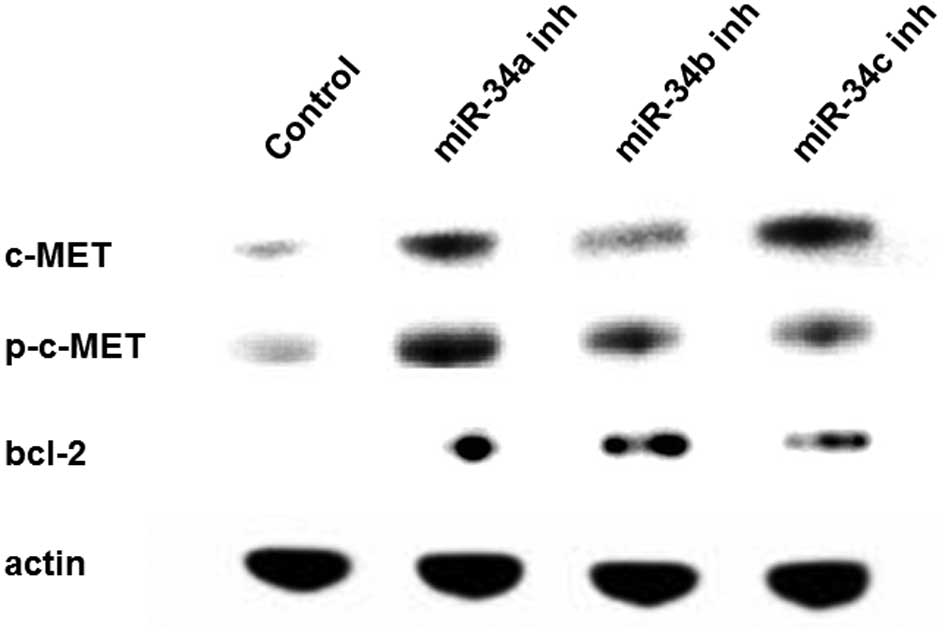
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive tumor with a dismal prognosis, and the molecular alterations involved in this disease remain unknown. We previously reported that microRNA-34s (miR-34s) are methylated and downregulated in MM and may play an important role in the carcinogenesis of MM. In this study, we downregulated miR-34s in human mesothelial cells to investigate the cellular effect of miR-34 knockdown. For the cell study, we used LP-9, a human mesothelial cell line, and three human primary-cultured mesothelial cell lines. RNA-based miR-34a, -34b and -34c inhibitors were transfected into these cells, and their effects on proliferation and invasion were evaluated. A scramble RNA oligonucleotide was used as a control. The protein expression status was estimated using western blotting. After miR-34 inhibitor transfection, miR-34a, -34b and -34c were downregulated in all the examined mesothelial cell lines. miR-34 inhibitor transfection significantly increased cell proliferation in all of the mesothelial cell lines, compared with the scramble control. The invasive ability also increased in the miR-34 inhibitor transfectants, compared with the scramble control, in the LP-9 cell line. Western blotting confirmed the upregulation of c-MET, phospho-c-MET, and bcl-2 proteins in LP-9 cells after miR-34 inhibitor transfection. In conclusion, our study showed that the downregulation of miR-34s induced an oncogenic phenotype in non-malignant mesothelial cells. The present study, together with the results of our previous report, strongly suggest that miR-34s play an important role in the early carcinogenic process involved in the transformation of human mesothelial cells to MM.

Astragaloside in cancer chemoprevention and therapy

Epigenetic Regulation of miRNA Expression in Malignant Mesothelioma: miRNAs as Biomarkers of Early Diagnosis and Therapy. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Sirolimus induces apoptosis and reverses multidrug resistance in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro via increasing microRNA-34b expression

A comparison between the effects of over-expression of miRNA-16 and miRNA-34a on cell cycle progression of mesothelioma cell lines and on their cisplatin sensitivity - ScienceDirect

Melodic maestros: Unraveling the role of miRNAs in the diagnosis, progression, and drug resistance of malignant pleural mesothelioma - ScienceDirect

Deciphering signaling pathway interplay via miRNAs in malignant pleural mesothelioma - ScienceDirect

Emerging role of exosomes in cancer progression and tumor
Blockage of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and upregulation

Sirolimus induces apoptosis and reverses multidrug resistance in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro via increasing microRNA-34b expression
MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. - Document - Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine

Vaspin regulates the osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 through the PI3K-Akt/miR-34c loop

Versatile role of miR-24/24-1*/24-2* expression in cancer and

/cms/asset/a396d422-3c42-41ba-b
Exosomes and ferroptosis: roles in tumour regulation and new

MicroRNAs in Human Cancer