Alveolar macrophages help CD8+ T cells go (anti-)viral
$ 21.50 · 5 (600) · In stock

The human immune system is a highly complex network of cells, signals, and responses that is tightly regulated to ensure that the body can fight off infection without damaging its own tissues. Now, researchers from Japan report a new way in which the immune system protects lung tissue from viral infections.
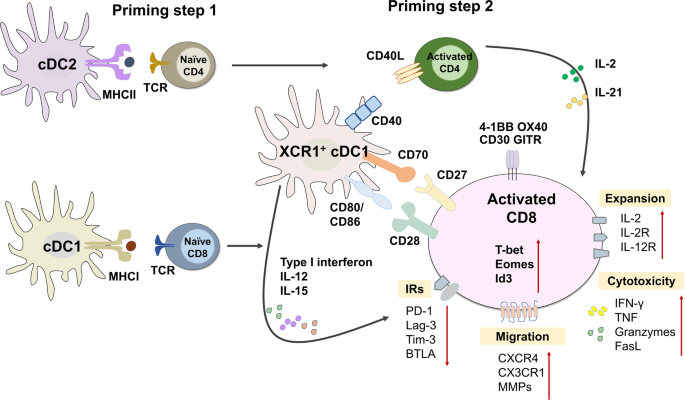
T cells in health and disease Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy

Helminth exposure protects against murine SARS-CoV-2 infection through macrophage dependent T cell activation

Alveolar macrophages instruct CD8+ T cell expansion by antigen cross-presentation in lung - ScienceDirect

Natural killer' immune cells can modify tissue inflammation: Study

Tissue resident memory T cells in the respiratory tract - Mucosal Immunology

Induction of Autonomous Memory Alveolar Macrophages Requires T Cell Help and Is Critical to Trained Immunity - ScienceDirect

JCI - Cross-presenting CD103+ dendritic cells are protected from influenza virus infection

CD8+ T cell activation in cancer comprises an initial activation phase in lymph nodes followed by effector differentiation within the tumor - ScienceDirect

Macrophage - Wikipedia
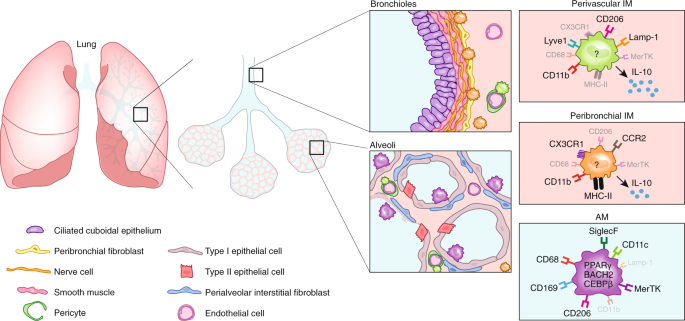
Does tissue imprinting restrict macrophage plasticity?
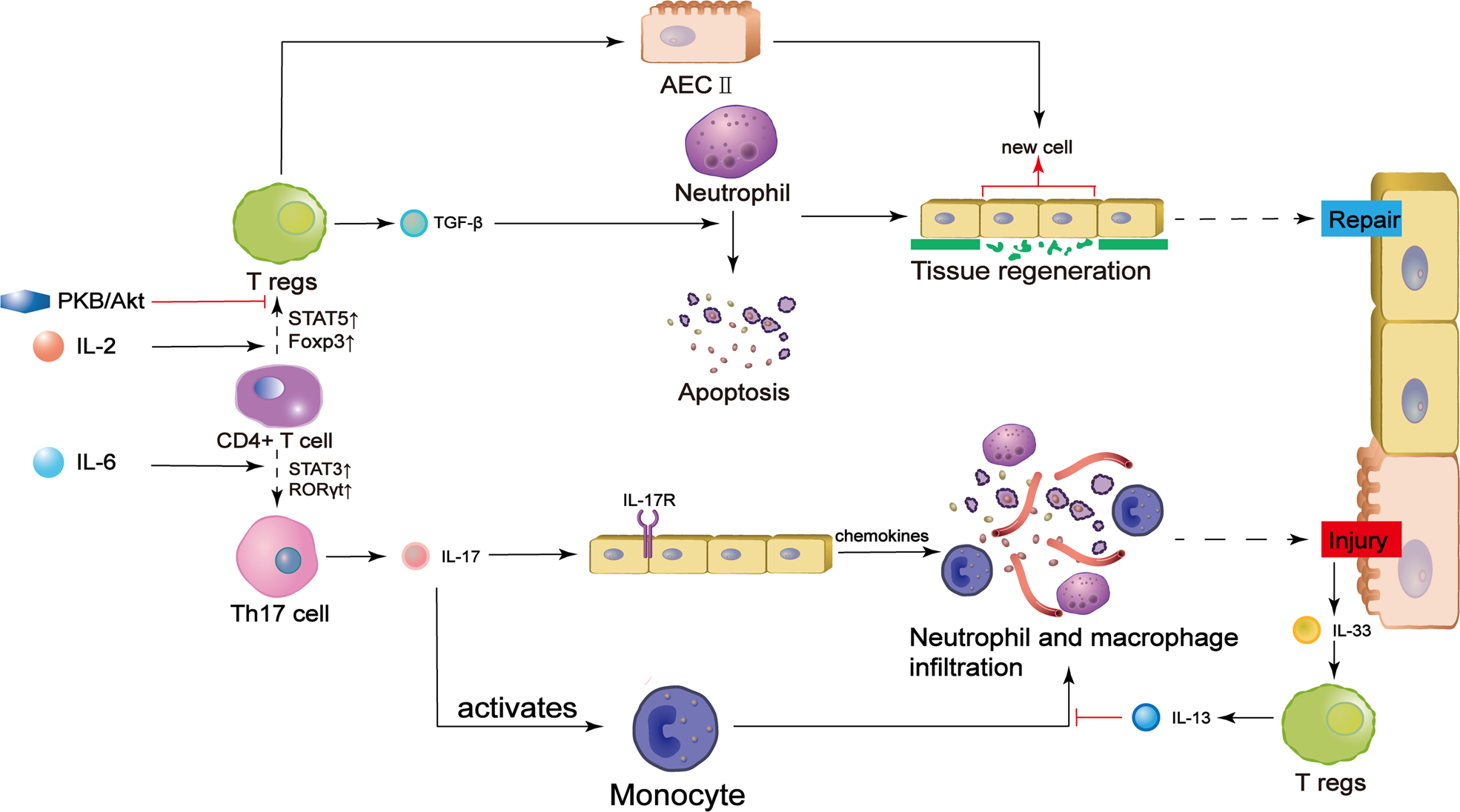
Regulatory T cell and macrophage crosstalk in acute lung injury: future perspectives